Overview
This is yosi from Chillout with Beats.
VCV RackThis is the eleventh article.
Click here for previous article
Continuing from the last time, we will introduce recommended modules.
this time too, Mutable Instruments Was the baseAudible Instruments.
(When will you hear the voice saying that you will introduce another module ...)
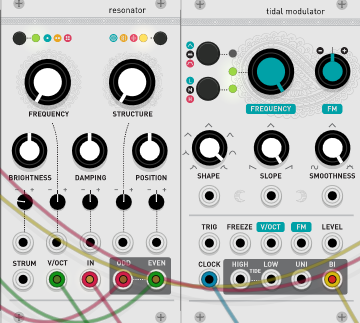
Resonator (Rings)

This time, I thought it would be easy to make a sound and it would be easy, but when I was careful, it was in a fairly hidden command state ...
(Dandruff in the back)
The explanation of the manual is as follows.
The ring is a resonator and is an important element at the core of some physics modeling techniques.It converts an external, pitchless excitation audio signal (such as a click, a burst of noise, or one captured by a contact microphone) into a full-bodied pitched sound.A ring is a bar, tube, or bundle of strings that vibrates with an external signal.
Key Points
It ’s deep, butMutable InstrumentsThen, it is unusual and easy to make a sound.
4Put the audio source (electric piano or acoustic guitar loop is recommended) in the IN of⑤If you connect the ODD to a mixer etc., you will get a pleasant sound. (Like a flanger)
Lightly hereCYou won't get tired of listening for about 30 minutes just by moving. (It's great if you move it loosely with an LFO)
I recorded it for a moment.In the electric piano loopCI'm just moving the knob.
However, we use three inputs to get the most out of it.
(XNUMX) STRUM is a trigger signal, (XNUMX) is a V / OCT input, and IN input is an audio signal.
STRUM of ② is good for click sound without pitch.
(I think DrumKit's Closed Hihat is good)
16-Step SEQ can easily output V / OCT.

I made it for fun. (I played a little too much)
Polyphony and synthesis methods
ACan increase the number of pronunciations with Polyphony selection.Green is mono, yellow is 2 sounds, and red is 4 sounds.If you increase the number of pronunciations, the sound will be hard to break when you play a long release sound.
BThere are three types of resonators.
modal resonator
Modal synthesis works by simulating the resonance resonance of a vibrating structure.That is, a way a string or plate absorbs a particular frequency while "ringing" at another frequency called a mode.When you play a string, hit a drum, or hit a tube, a short burst of blow / impact energy contains many frequencies.Some of these go out of mode and are absorbed.Some of these stimulate the mode and produce a sound with a stable pitch.Each mode corresponds to a harmonic or partial sound in the spectrum of the sound and is modeled by a bandpass filter.The Q factor of the filter determines how long the vibration of the corresponding partial sound lasts.The different materials and structures are characterized by the different relationships between the frequencies of those modes that the ring reproduces.
Sympathetic strings
Some interesting stringed instruments (such as sitar and sarod) use strings that only respond to the vibrations of other strings, rather than the musician playing or playing them directly, adding overtones and bass to them. Rings simulates this phenomenon with a large number of virtual strings (made with comb filters) that allow you to add extra tones to the incoming audio signal.The tuning ratio of these strings can be changed.
Modulated / inharmonic string
This last method is probably best known because it is based on the extended Karplus-Strong method.The excitation signal is sent to a comb filter with an absorption filter and is absorbed at the laces and ends.But for a wider variety of sounds, Rings adds three additional elements to this classic.An all-pass filter is applied to the delay loop to shift the partial position, reproducing the tension of the piano strings and the completely anharmonic tone of the vocals.
CONTROLS, INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
I will use the official image.

A.Polyphony Settings Select the monophonic, duophonic, and quad-refonic behavior.
Resonator type.Choose from modal, sympathetic, and stringed instruments.
C.Coarse frequency adjusted in semitones.This control spans 5 octaves.
D.In harmonic structure modal resonators, this parameter controls the frequency ratio between partials (so the perceived structure – plates, bars, strings).For sympathetic string resonators, this parameter controls the set of frequency ratios between all strings (with an octave or one-fifth virtual notch).Finally, in the Modulation / Inharmonic String Resonator, this parameter controls the amount of modulation and partial detuning.
E.Simultaneously acting a low-pass filter on the brightness exciter signal (closed at 8 o'clock, fully open at 12 o'clock) and damping filter (or higher mode above the rest of the potentiometer).Low values simulate materials like wood and nylon.High values simulate materials such as glass and steel.
F.Dumping.Controls the decay time of the sound from less than 100 milliseconds to about 10 seconds.
G.Excited position.Controls which point on the string / surface the excitation is applied to.When the excitation is applied in the middle of the surface, the symmetry causes the even harmonics to cancel each other out, creating a "hollow" sound reminiscent of a square wave.This setting will remind you of the PWM control of the square oscillator, or the comb filter effect of the phaser.
H. Attenuator for CV input.
1.Resonator parameter CV input. The FREQUENCY CV input is normalized to a voltage of 1/12 V so that the attenuator can be used for finer frequency control when the patch cable is not inserted.
2.Strum trigger input for polyphonic operation.Whenever a trigger is received on this input, the module freezes the currently playing voice, attenuates it, and begins a note with the next voice. Normalized to V / OCT input step detector and IN input transient detector.
3. V / oct CV input.Controls the main frequency of the resonator.
4.Audio input for the excitation signal.Modular level is expected! Normalized to a pulse / burst generator that reacts to record changes in the V / OCT input.
5.Odd and even audio output.In monaural mode, these two outputs carry two complementary components of the signal: odd and even partials by modal resonator, dephase component by picking position and pickup placement by string resonator.Polyphonic mode splits the signal into odd-numbered and even-numbered strings / plates.To split the signal, you need to insert a jack at each output. If only one jack is inserted, both signals will be mixed.
Summary
You can get a pretty interesting effect as a simple effector, but it's too deep.
I feel like I'm going crazy if I do it while connecting the patch cable with the real thing without knowledge ...
However, I feel that there are quite a lot of possibilities, and like other modules, the range of sounds that come out will really expand when it becomes a little usable.
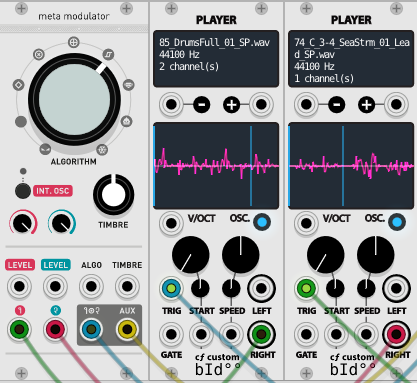
I made something like this using Resonator, Meta Modulator and Tidal Modulator.
Don't you feel like Aphex Twin in the 90's just for a moment?
Kick is a Synthtic Bass Drum and only Reverb uses FL Studio's Fruity Convolver.
Everything else is VCV Rack.
Comment