Native Instruments Massive X Manual Japanese Routing Edition
This is yosi from Chillout with Beats.
I will tell you the Routing edition in Japanese and some videos.
Click here for other Japanese localization manuals.
ROUTING
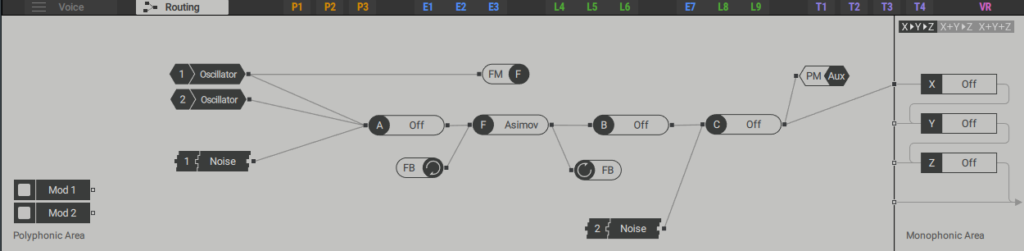
"Routing" is this part.It can be routed freely and is really easy to use.
1. ROUTING
MASSIVE X is an open architecture semi-modular synthesizer.This means that you can freely arrange and connect modules to easily perform different compositing techniques, allowing you to design and explore sounds without constraints.
It can be combined using techniques such as wavetable synthesis, phase modulation (also known as PM, FM or frequency modulation), subtractive synthesis, physical modeling, various types of waveform shaping, or distortion.
Modules are deployed and connected on the Routing page.Here you can combine all MASSIVEX sound generators and processors to create sounds.
2.OVERVIEW OF THE ROUTING PAGE
The following overview shows the two main areas of the routing page, the polyphonic area and the monophonic area.The polyphonic area is used to define a signal path that is processed independently for each voice played.The monaural area contains three stereo effects that are applied globally to the sum of all polyphonic voices.
(1) Polyphonic area:Contains modules that can be used to define the signal path for polyphonic voice.To complete the signal path, one or more module outputs must be connected to the input in the monaural area (1).The following modules are in the polyphonic area.
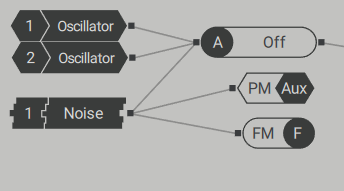
Generators and Processors: Oscillators, Noise Sources, Filters, Insert Effects
Available in the polyphonic area.The black module represents the generator and the gray module represents the processor.The icon displayed on the module is also on the corresponding icon.
Module Panel For more information, see Generators and Processors.
PM Aux bus:Makes the oscillator's phase modulation input accessible by routing.
In this way, you can use any source in the signal path to apply phase modulation to the wavetable oscillator and try out noise, feedback, and effects in this application.See PM Aux Bus for more information.
![]()
FB (Feedback) loop:Makes the global feedback loop accessible within the routing.in this way
You can create a polyphonic feedback loop around the module to add chaotic non-linear behavior.
This feature is also useful for physics modeling sounds, especially when combined with modeling.
Comb filter See Feedback Loop for more information.

Mod Source:You can assign any modulator to the modulation source by dragging and dropping.This allows the modulator to be used as a signal path generator.
For example, you can use the OSC mode switcher LFO as an additional oscillator, or the Exciter Envelope as an exciter for the Comb filter.See Modulation Sources for more information.
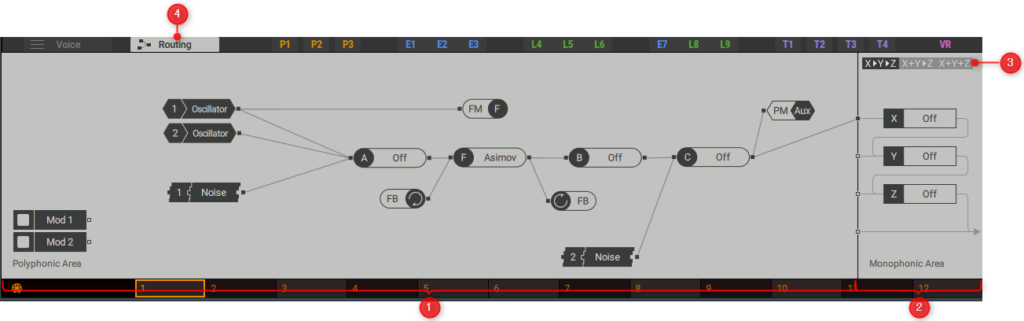
(2) Monophonic Area:Sum the polyphonic audio and apply the three stereo effects X, Y, and Z before sending the output signal to the host.The monaural area has four inputs, one for each stereo effect and one that is sent directly to the host.
(3) Routing option:Three different routing options define the order of effect of the signal path. X> Y> Z connects the three effects, and X + Y> Z sends the sum of the X and Y effects to the Z effect. X + Y + Z sums all three effects.
(4) Routing:Open the routing page in an editor.
3.GENERATORS AND PROCESSORS
The generators and processors in the polyphonic area of the routing page are the basic components you can use to build your sound.They consist of oscillators, noise sources, filters, and insert effects.
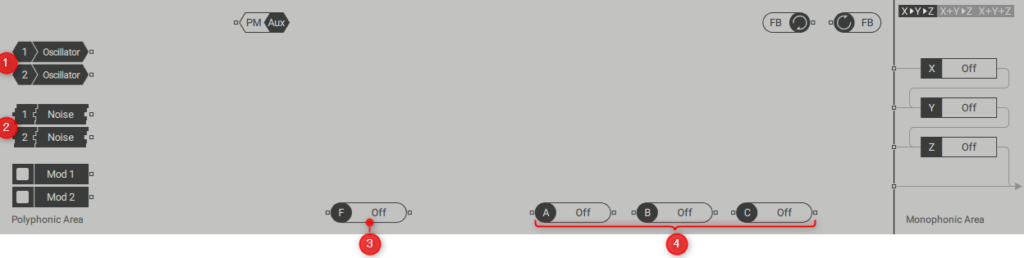
(1) Oscillator:Wavetable oscillators 1 and 2 are generators, each with a single output.They can be connected to a processor or bus in the polyphonic area, or directly to an input in the monophonic area.
(2) Noise source:Noise sources 1 and 2 are generators, each with a single output.
They can be connected to processors and buses in the Olympic area, or directly to the inputs in the monophonic area.

(3) Filter:A filter is a processor that features a single input and a single output.It can be connected to a polyphonic area generator, processor, bus, or directly to a monophonic area input.Filter types Asimov, Blue Monark, Groian and Scanner have a special FM bus for routing.
You can also connect any source of the signal path here and apply audio rate modulation to the filter frequency.This is also known as filter FM (frequency modulation).Filter FM produces rich overtones and distortion effects.
(4) :The three insert effects A, B, and C are processors with a single input and a single output, respectively.They can be connected to polyphonic area generators, processors, buses, or directly to monophonic area inputs.You can also use them as generators by selecting OSC or PM OSC for the insert effects.
4.PM AUX BUS
The PM Aux bus allows you to use any source in the signal path to apply phase modulation to the wavetable oscillator.For example, you can try noise, feedback, and effects.
The Polyphonic Area on the Routing page of the PM Aux bus has a dedicated module, and the Wavetable Oscillator panel has additional controls.
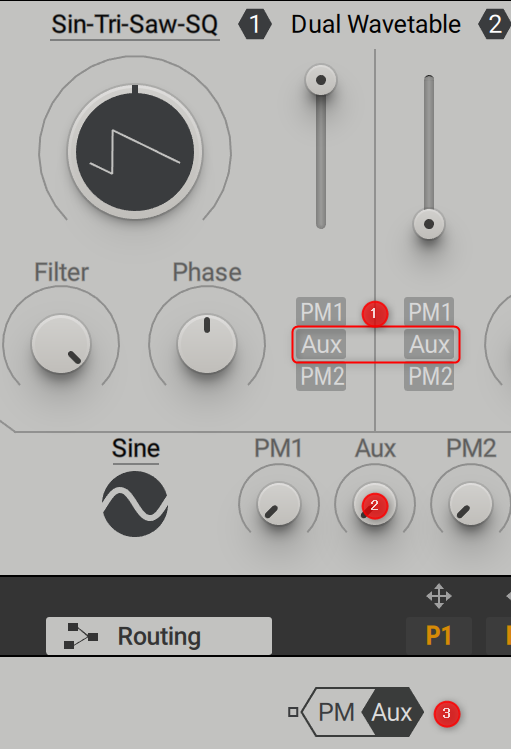
(1) AUX assignment: Assigns the signal received at the input of the PM Aux bus in the polyphonic area of the routing page to the corresponding wavetable oscillator.
(2) Aux modulation amount: Adjusts the amount of phase modulation applied from the PM Aux bus to the Wavetable oscillator.
(3) PM Aux Bus: This bus has a single input that sends a signal to the phase modulation function of the Wavetable oscillator.It can be connected to generators and processors in the polyphonic area
5.FEEDBACK LOOP
A Feedback loop in the Polyphonic Area of the Routing page facilitates the connection from the module's output to its input.You can chain any number of modules into the feedback loop.In this way, you can add chaotic, non-linear behavior to your sound.Feedback loops are also useful for physics modeling sounds, especially when combined with Comb filters. Since the Feedback loop is polyphonic, it is processed independently for each voice you play.
In this way, you can play chords and superimpose notes that overlap with feedback.
The feedback loop can freely connect to the polyphonic area of the routing page using two FB modules.
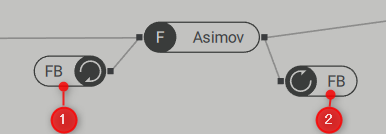
(1) FB (Feedback) Loop Output: This bus has a single output that receives a signal from the feedback loop input.You can connect to generators, processors, and buses in the polyphonic area.
(2) FB (Feedback) Loop Input: This bus has a single input that signals the feedback loop output.You can connect to generators and processors in the polyphonic area.
In the above example, the Asimov filter output is connected to the FB input (2) and the FB output (1) is connected to the Asimov filter input.This creates a feedback loop around the filter, making it sound distorted, and behaves in an unexpected but interesting way.
5.1. Feedback Level Control
Use the FB level control on the amplifier module panel to control the amount of feedback.

(1) FB (Feedback) level: Adjusts the volume of the feedback loop.In this way, you can control the chaotic behavior and distortion caused by feedback.
(2) High-pass filter: Enables a high-pass filter that cuts the low-frequency components of the feedback loop.When activated, you can prevent the feedback loop from being overloaded with excessive bass.
6. MODULATION SOURCES
You can use the MASSIVE X modulator as a signal path generator by using the modulation source in the polyphonic area of the routing page.For example, you can use a switcher.
An OSC mode LFO as an additional oscillator, or an Exciter Envelope as an exciter for a comb filter.
To assign a modulator to a polyphonic area modulation source:
1. Click the modulator arrow icon (1) to select it, then click the modulation source slot (2) in the polyphonic area to assign it.
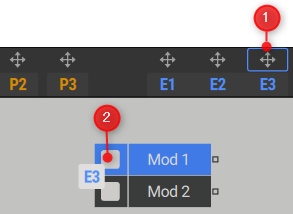
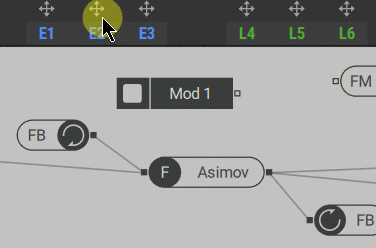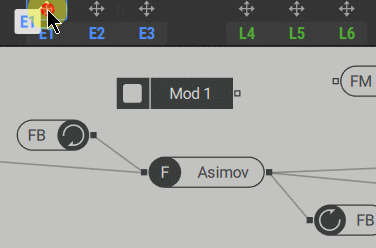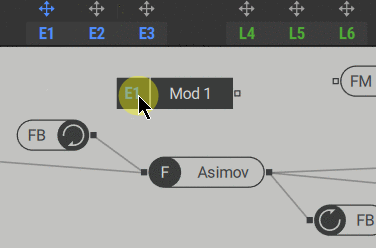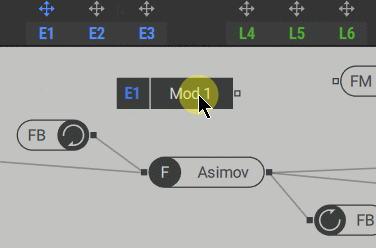
The signal generated by the modulator comes from the output of the modulation source and can be used anywhere in the signal path.
7. USING THE ROUTING PAGE
The Routing page places and connects the individual building blocks or modules that make up the synthesizer.The connection between the input and output of the module is established using wires.The output can be connected to any number of inputs and vice versa.In this way, you can distribute the signal to multiple destinations or mix multiple outputs on the same input.
7.1. Routing Workflows
To connect between modules:
1. Click Output to see all connectable inputs.
2. Click the input to which you want to connect the output.
To establish an exclusive connection to the input, delete all existing connections to the input.
1. Click Output to see all connectable inputs.
2. Right-click the input for which you want to connect the output exclusively.
To remove a wire:
• Double-click the wire you want to delete.
To remove all connections from the module
• Double-click on the module for which you want to remove all connections.
You can also disable or bypass the module directly on the Routing page.This allows you to quickly hear the effect of the generator or processor on the sound.
To bypass the module while maintaining connectivity
• Right-click on the module you want to bypass



Comment