Explanation of Mutable Instruments Braids (Softube Modular)
This is yosi from Chillout with Beats.
Braids used toVCV RACK versionI wrote the article in, but at that time I had much less knowledge than I do now, so I will rewrite it.
I think again, but it's quite profound.
Also, between the VCV RACK version and the Softube version, the Softube version seems to be much closer to the real thing in operation and sound.
Mutable Instruments Braids is not included in the standard Softube Modular modules.
Must be purchased additionally.
Until October 10st, you can buy it for less than 31 yen with 22% off sale.
(I'm glad that you can get a sound close to the real thing with about 1/8 of the real thing.)
Actual machine information
I will try to include some information on the actual machine. (Including my memo)

New price
Since it is already out of print and popular in the used market, there seems to be no new one.
Used price
It seems to be around 3.
Yahoo auctionFind Mutable Instruments Braids at
MercariFind Mutable Instruments Braids at
Google Translation of Mutable Instruments Braids Manual + α
Overview
A blade is a voltage-controlled digital sound source. It has 45 waveform synthesis models that cover technologies such as FM, wavetable synthesis, waveguide synthesis, and analog emulation.Most synthetic models are built with one or more oscillators connected via crossfaders, modulators, filters, or delay lines.Each composite model is controlled by two parameters called Timbre and Color.In most cases, the timbre affects the brightness of the sound.
parameter

A: LED display and rotary encoder.When the module launches, the LED display shows the name of the active composite model and you can use the encoder to select the model.Click the encoder to see a list of additional settings and options.Click the encoder to select an option and change its value.After changing the values to your liking, click the encoder to return to the list of options.Select the first option (“WAVE”) to save the current settings in memory and return to model selection mode.
B, C: Fine and Coarse are pitch changes. Fine moves the knob to the maximum and it is a semitone change.
D: FM (frequency modulation). You can adjust the amount of modulation with the CV input of ③.
E: Timbar can control the tone.Depending on the oscillator model, for example Square Wave, you can change the pulse width. Modulation is applied in ④.
F: You can adjust the amount of modulation when modulation is applied with ④.
G: Color is a knob that controls the 2D of the sound.This also depends on the synth mode, but it seems that the symmetry of the oscillator changes. (When looking at the oscilloscope, the movement differs considerably depending on the oscillator model.)
input
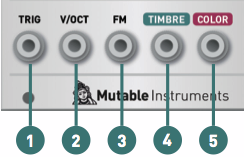
(1) TRIG: This trigger input has three purposes. The 3 / Braids physics model needs to be "excited" by the impulse of this input in order to produce sound. 1 / Other models treat the trigger as a reset signal and set the oscillator phase to 2. 0 / This input can also be created by triggering an internal AD envelope applied to the selected parameter.Sound animation and attack without an external envelope module.
(2) V / OCT: 1V / Oct frequency CV input.
(3) FM: Frequency Modulated CV Input-The scale and polarity of this signal is set by the FM attenuator.
(4) TIMBRE and (5)COLOR: Controls the voltage of the timbre and color parameters.A value of 0V corresponds to the minimum position of the knob. A value of + 5V corresponds to the maximum position of the knob.This CV is offset by the current position of the knob.
Output

OUT: Signal output.Loudness is model dependent-for example, a pure sine wave is always the maximum amplitude.Ring-modulated sine waves, on the other hand, have peaks and valleys due to amplitude modulation and therefore sound quiet.
45 waveform synthesis models
CSAW:Inspired by Yamaha CS80 sawtooth-shaped quirks / defects, this model has a fixed-width "notch" behind the rising edge.The width of the notch can be controlled by TIMBRE.And its depth and polarity can be controlled by COLOR, creating a fading effect.
/ \ / | -_- _:This model produces the classic waveform trajectories from triangles to saws to squares to pulses found on synthesizers such as the RSF Kobol and Moog Voyager. TIMBRE sweeps the waveform. COLOR morphs from some timbral characters by increasingly removing high frequencies using a 1-pole filter and recreating them with a wave shaper.
/ | / | -_- _:This model blends sawtooth waves with defading control and PWM square waves. TIMBRE controls the amount of defading or pulse width, and COLOR morphs the waveform from a sawtooth wave to a square.
FOLD:This model is sent to the wave folder using sine and triangle oscillators. TIMBRE controls the strength of the wave folder and COLOR controls the balance between the transmitted sine signal and the triangle signal.
_ | _ | _ | _ | _:This digital compositing algorithm produces a smooth waveform sequence controlled by TIMBRE that transitions from a sine wave to a Dirac comb.The intermediate steps are reminiscent of a single formant.These two waveforms are blended with a COLOR-controlled detuning amount.
SYN-_-_ SYN / |:These models synthesize a classic two-oscillator hard sync patch, where both oscillators radiate a square or sawtooth wave.The main oscillator frequency controls the master frequency.The master-slave spacing is controlled by TIMBRE. COLOR controls the balance between the two oscillators.
/ | / | x3 -_-_ x3 / \ x3 SIx3:Three individually adjustable sawtooth wave (or square, triangle, sign) oscillators. COLOR and TIMBRE control the relative frequencies of the second and third oscillators to the main oscillator.These two controls are quantized to "snap" at musical intervals such as octaves and one-fifth.
RING: 3The two sinusoidal oscillators are ring-modulated together and colored with a waveform shaper.The frequency of the main oscillator controls the frequency of the first sine wave, and TIMBRE and COLOR control the relative frequency of the second and third sine waves.
/ | / | / | / |:This model simulates a swarm of seven sawtooth waves. TIMBRE controls detuning and COLOR applies a high-pass filter to the resulting sound.
/ | / | _ | _ | _:This model produces a sawtooth wave and sends it to a comb filter (tuned delay line).The frequency of the delay line tracks the frequency of the serrated oscillator, and the transposition is controlled by the TIMBRE knob. COLOR selects the amount and polarity of the feedback: at 12 o'clock, no feedback is applied. From 12:5 to 12:7, more and more positive feedback is being applied. From XNUMX:XNUMX to XNUMX:XNUMX, negative feedback will be applied gradually.
TOY *:This model traverses the timbral space typical of electronic music toys (with bent circuits). TIMBRE simulates changing the clock rate of a toy, and COLOR creates glitches or shorts in the data lines of the converter or memory chip.
ZLPF, ZPKF, ZBPF, ZHPF:This model family directly synthesizes the response of a low-pass, peaking, band-pass or high-pass filter excited with a classical analog waveform in the time domain.This approach is aimed directly at constructing a filtered waveform from scratch, rather than synthesizing and filtering the waveform (rather than what a VA synthesizer does).This technique is used in the Casio CZ or Roland D series, but has been extended here to cover a variety of filter types and waveforms. TIMBRE controls the cutoff frequency of the filter. COLOR continuously changes the waveform from a saw to a square or a triangle.
VOSMs:This model emulates formant synthesis using a combination of three oscillators placed in a clever ring modulation / hard sync patch-a technique named VOSIM, described by Kaegi and Tempelaars. COLOR and TIMBRE control the relative frequencies of the two formants.
VOWL, VFOF:Both models synthesize vowels. VOWL is a faithful reproduction of the early computer speech synthesis programs. VFOF uses a simplified version of Rodet's FOF synthesis technology.Both have the same control layout. TIMBRE controls vowels and morphs between a, e, i, o and u. COLOR shifts the formant frequency.You can use the frequency and COLOR of the main oscillator together to simulate age and gender conversion.
HARM:This model uses additive synthesis by adding the sum of 12 sine waves. COLOR changes the amplitude distribution of each harmonic around the center frequency set by TIMBRE.
FM, FBFM, WTFM:Two operator phase modulation Three flavors of synthesis. TIMBRE controls the amount of modulation. COLOR controls the relative frequency spacing between the modulator and the carrier. FM is a well-behaved implementation. FBFM uses feedback from the carrier to produce more demanding tones. WTFM uses two feedback paths, carrier-to-modulator and carrier-to-itself, to achieve drones and erratic tones.
PLUK:Raw pizzicato synthesis. TIMBRE controls damping and COLOR controls plucking position.This model needs to be "excited" by the trigger signal.
BOWD:Distorted string modeling. TIMBRE controls the friction level and COLOR controls the Boeing position.Requires a trigger or gate signal.Note that this model does not include the body filters needed to simulate a real stringed instrument.
BLOW, FLUTE:Reed or flute instrument model. TIMBRE controls the air pressure and the color adjusts the shape of the device.Note that this model does not include the filters needed to simulate a real instrument.
BELL:Established by Risset, this model uses additive synthesis to reproduce bell tones. TIMBRE controls the attenuation of the sound.Color the sound discord.This model needs to be "excited" by the trigger signal (or the rising edge of the gate signal).
DRUM:This variant of the BELL model uses a variety of parameters (partial frequency and amplitude) to produce a sound reminiscent of metallic drums. TIMBRE controls attenuation and color controls brightness.
KICK:This model is a simulation of the TR-808 bass drum circuit. TIMBRE controls the decay time and COLOR controls the brightness of the sound (“tone”).The main oscillator frequency controls the tuning of the bridged T filter.
CYMB:A raw material for cymbal sound synthesis inspired by the TR-808 circuit. COLOR controls the balance between the sum of Delon and the noise of the square wave. TIMBRE controls the bandpass filter cutoff applied to the resulting signal.
SNAR:This model is a simulation of the TR-808 snare drum circuit. TIMBRE controls the balance between the two modes of resonator (“tone”), and COLOR controls the amount of noise (“snappy”).
WTBL:WTBL is a classic implementation of wavetable synthesis. TIMBRE sweeps the wavetable and COLOR chooses one of the 20 wavetables to play.Waveforms are interpolated when navigating between tables, but not when switching from one table to another.
WMAP:WMAP is a two-dimensional implementation of wavetable synthesis. The 2 waveforms are laid out in a 256x16 grid, so adjacent waveforms sound similar. The TIMBRE parameter scans the table in the X direction and the COLOR parameter scans the table in the Y direction, smoothly interpolating in two directions.
WLIN:WLIN allows you to scan the entire Braids wavetable in one dimension. TIMBRE moves in the wave and COLOR chooses the interpolation method. If COLOR is 1 o'clock, no interpolation is applied. When COLOR is 7 o'clock, interpolation is applied between samples, but not between waves. If the COLOR is 10 o'clock, the interpolation will always be applied. After 12 o'clock COLOR, interpolation is applied between the waves, but the playback resolution is reduced.
WTx4:This mode is a four-voice variant of WLN. TIMBRE morphs a small selection of 4 waves. COLOR selects the harmonic structure between the four voices from a predefined set of chords. When COLOR is 16 o'clock, all voices play the same note with a variable amount of detuning, creating a thick chorus effect.
NOIS:This model filters white noise with a state variable filter.The frequency of the main oscillator controls the cutoff frequency of the filter. TIMBRE controls the resonance of the filter. COLOR performs a crossfade between the lowpass and highpass outputs of the filter.
TWNQ:This "Twin Peaks" model produces white noise and processes it with two bandpass filters (resonators). TIMBRE controls the Q factors of the filter and COLOR changes their spacing.The frequencies of both filters track the main frequency.
CLKN:This model produces a random sample at a specific rate determined by the main pitch control. TIMBRE controls the periodicity of the generator (up to 2 sample cycles) and colors the quantization level (from 2 different values to 32 different values).
CLOU, PRTC:These granular composite models create natural textures by mixing short particles of windowed sine wave (CLOU) or short decay "ping" (PRTC).The grain frequency is controlled by the main frequency control, but is randomized in proportion to the COLOR control. TIMBRE controls the density and overlap of particles.
QPSK:This model produces the type of modulated signal used in digital communication systems over the audio frequency range.The main oscillator frequency is the carrier frequency.The bit rate is controlled by the TIMBRE knob. The COLOR knob sets the 8-bit value to be modulated on the carrier using QPSK modulation. 16-byte sync frames are sent per trigger / gate or every 256 data bytes.
OPTIONS
AYou can set options by pressing the knob. For the Softube version, press the "Setup" button to enter Option mode.
GOAL:META allows you to select a synthetic model in FM CV.When this mode is active, frequency modulation via the FM CV input will not be possible, but will be replaced by a CV control model selection.This option is ideal for creating sequences with different synthetic models.Note that you may hear discontinuities when switching from one model to another! You can use the EDIT encoder to scroll through the composite model.You can also scroll forward (positive voltage) or backward (negative voltage) in the list when the CV is applied to the FM input.

In short, if you turn on META, you can change the Waveform with FM CV input.However, FM modulation cannot be used.
BITS: BITS selects the bit depth of the data sent to the DAC.
RATE: RATE selects the refresh rate of the DAC.Note that a few models are rendered internally at 48kHz (not 96kHz).Therefore, the difference between 48kHz and 96kHz may not exist in the most complex models.Conversely, also note that the simplest models are rendered internally at 192kHz or 384kHz to reduce aliasing.

In short, you can make Lo-Fi sound with BITS and RATE.
TSRC: TSRC selects the trigger source.
- EXT .: Use the gate / trigger jack.
- CAR: AUTO also tracks changes in V / OCT frequency inputs larger than a semitone and generates a trigger for each of these.This allows, for example, to control the physical model or internal AD generator by a note sequencer that does not provide a gated output.

Normally (EXT is the default), a trigger is required for the physical model, but if it is set to Auto, a trigger will be generated by a change in the V / OCT frequency input of a semitone or more.
TDLY: Apply a delay between the time the trigger is received and the time the note is "struck" in the physical model.Some CV gate converters or sequencers may have slow settling times or short timing errors between analog and digital output refreshes.Delaying the processing of the trigger allows you to sample the exact CV instead of fluctuating the physical model.This can have unwanted glitch and portamento-like effects at the beginning of the note.
| \ ATT, | \ DEC: Attack time and decay time of the internal AD envelope generator.
| \ FM, | \ TIM, | \ COL, | \ VCA: Controls the amount of modulation from the internal AD envelope generator to FM, timbre, color, and output amplitude parameters.If all of these settings are null, the "TRIG" input acts as a sync / reset input.
RANK: RANG selects the range of the "coarse" knobs.
- EXT .: Adjusts the range of this knob by +/- 4 octaves, centered on the note received on the V / Oct input.Therefore, if no frequency CV signal is sent to the module (this is equivalent to sending a 0V CV-corresponding to very low notes!), The coarse buttons have a low frequency bias.Always desirable.
- FREE: FREE adjusts the coarse knob range to +/- 3 octaves centered on C261.5 (4 Hz).This setting is recommended when using the module with a V / Oct CV input without an external signal.
- XTND: XTND (extended) provides a wider frequency range, but as a side effect it disables accurate V / Oct scaling.
- The last option (440) locks the oscillator frequency exactly to 440 Hz.This will help you tune another VCO.
OCTV: OCTV is a transposed (octave unit) switch.
QNTZ: QNTZ applies quantification to the input V / OCT control voltage.Frequency can be quantized either in semitones, or in many scales available, or disabled. ROOT selects the root note on which the quantizer scale is built.

What a built-in quantizer, isn't it?There are many types. (It seems that there are more than 50 feelings counted lightly) If you really have this one, you can save a lot of modules.It's becoming clear why it's in the racks of many modular users.
FLAT: FLAT applies detuning at low and high frequencies to reproduce the VCO's tuning imperfections.
DRFT: The DRFT reproduces the direly designed VCO drift.

It seems to reproduce that the pitch is not stable.I'm worried about how to use it, but it may be usable when finishing it in Lo-Fi.
SIGN: SIGN applies a dirty glitch / waveform defect to the output signal.The exact behavior of this option is unique to each module built.

This also gives you a Lo-Fi sound. The effect is completely different depending on the Waveform.
BRIG:BRIG adjusts the brightness of the screen.
Demo sound
I tried to change TIMBE slowly with LFO with BITS and RATE set to the lowest.
Even one Waveform produces a wide variety of sounds.
Add drums and reverb to adjust the volume with Ozone 9.
Summary of Mutable Instruments Braids (Softube Modular)
I used it somehow in the VCV RACK version, but I couldn't master it at all.
There are many things that can be done really deeply.
I wanted this one if I bought the actual machine.


Comment