Overview
This is yosi from Chillout with Beats.
VCV RackThis is the XNUMXth article.
Click here for previous article
Continuing from the last time, we will introduce recommended modules.
This timeAudible Instruments OfModal SynthesizerI will only go.
This time, I prepared a demo sound source.
It's a fairly simple sound that you can listen to all the time.
If you haven't used it for the time being, please watch this video.
It has a pretty organic sound.
In terms of pluginsChromaphone 2I think it's close to.
Modal Synthesizer (Elements)
The real thing is like this.The price is about 64,000 yen.If you buy this, a power supply, and a box, it will exceed 10 ...
The sounds aren't the same, of course, but I'm really grateful that they can be enjoyed with software.
(If you think how to use it with software, it does not mean that you do not know how to use it even if you buy the real thing)
The real thing isAudible InstrumentsAnd VCV RackAudible InstrumentsThere was a video comparing.It sounds pretty close.Isn't it enough if it sounds so close for free?
Overview of Modal Synthesizer

Modal Synthesizer is a synth method that is close to the size of a physical modeling synthesizer.
Modal Synthesizer designs the sound by specifying the resonant structure (plates, strings, tubes, etc.), the characteristics of the materials from which it is made (rigidity, absorption, etc.), and how the structure produces the sound. can.
Each parameter
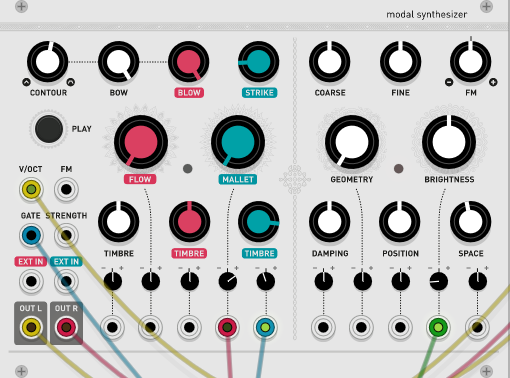
I will use the official image.
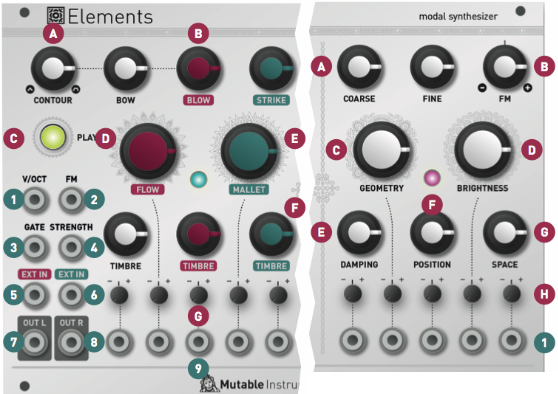
First of all, as a basic concept, Resonator refers to a filter. Exciter refers to the signal generator.
Exciter has BOW, BLOW and STRIKE (B in the above figure).
Resonator is Timbre (F in the above figure).
- The BOW generator synthesizes the sound of a bow that is damaging the material.Depending on the pressure of the bow, this combines the pure sound resulting from the interaction between the bow and the material with raw, scratched, granular noise.
- The BLOW generator synthesizes a continuous, noisy sound that blows, breathes, and is reminiscent of the wind.
- The STRIKE generator produces shocking bursts and percussive noise for hitting the oscillator.
Next, the front panel is divided into three sections.
- Control / performance section with the most important inputs / outputs.
- Exciter section where the signal is synthesized.
- A resonator that controls the frequency, amplitude, and Q value of the mode under the bonnet.
Control and exciter sections

AA simple envelope is applied to the sound produced by the BOW and BLOW exciters.This knob interpolates between the preset shapes of this envelope.Short AD envelopes can be longer or slower, morph into slower ADSR envelopes, or fade in to faster AR envelopes.
B. The BOW knob controls the amplitude of the scratch / boeing noise sent to the resonator.This is not just a gain.This control simulates an increase in bow pressure, producing a brighter, noisier sound. The BLOW knob controls the amount of granular blow noise sent to the resonator.Finally, the STRIKE knob controls the amount of percussive noise sent to the resonator.Setting this knob to a high value (after 2 o'clock) will send a percussive signal to the resonator, but it will be "bleeding" to the main output signal for a more spicy percussive sound.
C. PLAY button Press and hold this button to trigger the exciter and its envelope.This is the same as sending a positive gate to the GATE input.
D. Air FLOW of the BLOW This parameter can be described as a kind of wavetable scanning through various colors of noise. Automatically controlling this parameter with a CV (for example, from a LFO), will create a changing texture reminiscent of a turbulent air flow.
E.BLOW generator airflow.This parameter can be described as a kind of wavetable scan through noise of different colors.Automatically controlling this parameter with a CV (eg from an LFO) creates a changing texture that is reminiscent of turbulence.
- Actual samples of hammers, mallets and sticks.
- Physical model of a mallet.Play with or without attenuation.
- An electric physics model that played at various picking speeds.
- Physical model of particles bouncing on the surface
F. The TIMBRE knob on the BOW generator controls the smoothness or grain size of the bow material. The TIMBRE knob on the BLOW generator controls the pitch / granularity of the noise generator.Finally, the TIMBRE knob on the STRIKE generator controls the brightness / speed of the percussive sound.
G. Attenuator for CV input.
The main frequency of the sound is controlled by the COARSE / FINE knob in combination with the V / OCT and FM CV inputs.
Resonator section

A. COARSE frequency.Adjust in semitone steps.This control spans 5 octaves.Unquantized, FINE frequencies ranging from -2 to +2 semitones.
B. FM input. Attenuator This knob controls the amount and polarity of modulation applied to the frequency from the FM CV input jack.It has an exponential scale and decays very gradually as it moves away from the center position.
C. GEOMETRY. This important parameter controls the shape and stiffness of the resonant structure.It goes from the plate to the strings, to the bars / tubes, to the bells / bowls.
D. BRIGHTNESS. This parameter controls mute in high frequency mode.Low values simulate materials like wood and nylon.High values simulate materials such as glass and steel.
E. DAMPING controls How quickly energy dissipates through the material.Modulating this parameter with CV can reproduce the effect of blocking or muting the sound by manually blocking the vibrating surface.
F. POSITION Controls which point on the string / surface the excitation is applied to.When the excitation is applied in the middle of the surface, the symmetry causes the even harmonics to cancel each other out, creating a "hollow" sound reminiscent of a square wave.This setting will remind you of the PWM control of the square oscillator, or the comb filter effect of the phaser.
G. SPACE Controls the width of the stereo and the amount of reverberation of the algorithm applied to the sound.When this knob is set to the minimum position, one output channel will contain the exciter output and the other channel will contain the resonator output. As the SPACE grows, the sound of the vibrating surface is picked up at two different locations, creating a stereo effect. Increasing the SPACE will increase the angle between the two microphones. Before 1 o'clock, SPACE controls the amount of algorithmic reverb applied to the resonant signal and the decay time. Applying a very high CV when the SPACE parameter is in the maximum position creates a "freeze" effect and prevents the tail of the reverb from decaying.This can be used creatively to overlay notes layers to create chords.
H. Attenuverters for the CV inputs.
1. Resonator CV inputs.
Summary
Continuing from the last time, it is so deep that you cannot imagine it from its simple appearance.
Chromaphone 2It makes a sound similar to, but the degree of freedom is incomplete. (Although it is a thing)
If you understand it to some extent and then change the parameters, the width of the sound will widen.
After all, you should read the manual carefully.It is dangerous to understand.
Comment